Dynamic vs. Static: Impact on Portfolio Risk
Explore the differences between dynamic and static asset allocation strategies and learn how to manage portfolio risk effectively.
Dynamic vs. Static: Impact on Portfolio Risk
Dynamic and static asset allocation are two distinct strategies for managing investment portfolios, each with its own approach to balancing risk and reward.
Dynamic Allocation adjusts investments based on market conditions, aiming to reduce risk during downturns and capitalize on opportunities. It requires constant monitoring, involves higher transaction costs, and may trigger tax implications due to frequent trades. This approach suits investors who are active, knowledgeable, and comfortable with market fluctuations.
Static Allocation maintains a fixed percentage of assets, rebalancing periodically to stick to the original mix. It’s simple, low-maintenance, and avoids frequent trading costs, but it doesn’t adapt to changing market conditions, which can increase risk during volatile periods. This method is ideal for those who prefer a hands-off, consistent strategy.
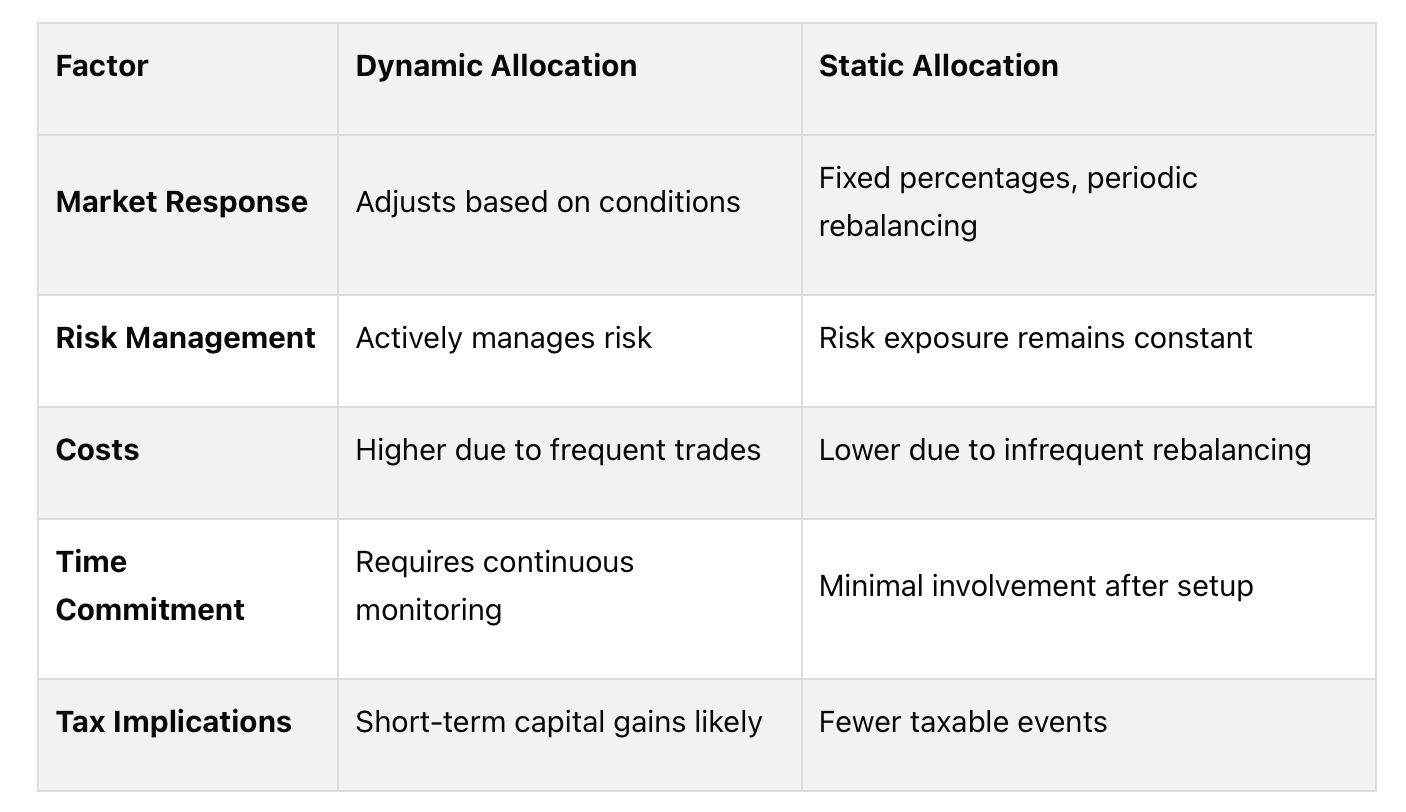
Quick Comparison
Key Takeaway: Choose dynamic allocation for flexibility and active risk management if you’re experienced and engaged. Opt for static allocation for simplicity and stability if you prefer a low-maintenance approach. A hybrid strategy combining both can balance risk and reward effectively.
The Mutual Fund Show: Dynamic Vs Static Asset Allocation
Dynamic Asset Allocation
Dynamic asset allocation takes a proactive approach to managing portfolios. Rather than adhering to fixed asset percentages, it continuously adjusts investments to reflect changing market conditions.
How Dynamic Allocation Works
This strategy relies on monitoring key market indicators and using models like Constant Proportion Portfolio Insurance (CPPI) to guide adjustments. For instance, during a market downturn, a dynamic approach might reduce exposure to equities and increase holdings in bonds, aiming to soften potential losses. These adjustments are typically automatic, triggered by predefined market conditions.
Rebalancing decisions are driven by mathematical models that set thresholds for when and how much to adjust. This removes emotional bias from the process. Unlike static allocation, which simply rebalances back to preset targets, dynamic allocation shifts strategically to seize opportunities or respond to risks in real time.
This adaptability plays a critical role in managing both risk and volatility effectively.
Risk and Volatility Management
Dynamic asset allocation shines during turbulent markets or bear phases. By actively reducing investments in underperforming or high-risk assets and reallocating to safer options, it helps limit portfolio losses. For example, in volatile periods, it might move funds from declining stocks to more stable assets like Treasury bonds or cash. However, this approach does come with a trade-off: the potential for “active risk”, where decisions might miss opportunities or mistime market shifts.
Compared to other strategies like buy-and-hold or constant-mix approaches, dynamic allocation often delivers better risk-adjusted returns, as evidenced by its position on the efficient frontier. This demonstrates its ability to manage volatility while maximizing returns.
Considerations for U.S. Investors
While dynamic allocation offers strong risk management benefits, U.S. investors face unique challenges when implementing this strategy. One major hurdle is the cost of frequent trading. Each adjustment generates transaction costs, including brokerage fees, bid-ask spreads, and potential market impact expenses. These can add up quickly compared to the lower costs of a static approach.
Additionally, frequent trades can trigger taxable events in taxable accounts, particularly short-term capital gains, which are taxed at higher ordinary income rates. This can significantly reduce net returns compared to the more favorable long-term capital gains rates.
Dynamic strategies also demand a higher level of expertise and time commitment. Whether using advanced software or relying on professional management, this approach may not be suitable for every individual investor.
For those who prefer a structured, rules-based system that minimizes emotional decision-making, dynamic allocation provides a framework to navigate changing market conditions more consistently. However, it’s important to weigh the added complexity and costs against the potential benefits.
Static Asset Allocation
Static asset allocation takes a fixed approach to portfolio management, standing in contrast to the more flexible dynamic allocation. This strategy sticks to predetermined percentages for various asset classes, regardless of how the market behaves.
How Static Allocation Works
Static allocation begins with setting a fixed mix of assets - like the well-known 60/40 portfolio - and sticking to it, no matter the market conditions. The process is straightforward: you choose an allocation and rebalance periodically to maintain it. This disciplined approach eliminates emotional decision-making and encourages the practice of buying low and selling high. In fact, research shows that 90% of return variation stems from the initial asset allocation decision.
The key idea here is consistency. Instead of attempting to time the market or predict economic trends, static allocation ensures steady exposure to your chosen asset classes. It’s a “set it and stick with it” philosophy that prioritizes simplicity over market timing.
Risk and Volatility Effects
While static allocation keeps your portfolio aligned with a target risk level, the actual risk you experience can shift dramatically depending on market conditions. This can create a mismatch between your intended level of risk and what you face, especially during periods of market turbulence.
For instance, during high equity volatility regimes (HVR), correlations between asset classes often rise by 0.3 or morecompared to calmer times. This means that during volatile periods, the diversification benefits you’ve carefully planned for might vanish when you need them the most.
“Market participants and investment professionals often lament that diversification benefits disappear when they are needed most.” - Masao Matsuda, PhD, CAIA, FRM, President and CEO of Crossgates Investment and Risk Management
Historical data from January 1954 to December 2018 underscores this point. In high volatility periods, equity and equity-like assets experienced roughly double the volatility seen in calmer markets. During these turbulent times, US equities delivered average monthly returns of just 0.19%, lagging behind the 0.35% risk-free rate of three-month T-bills. On the other hand, US government bonds performed far better, with average monthly returns of 0.58% - 1.6 times higher than their returns in low volatility periods. These figures highlight how different asset classes react to market stress, a nuance that static allocation strategies fail to address.
Benefits and Drawbacks
The appeal of static allocation lies in its simplicity. There’s no need for complex models, constant monitoring, or frequent trading decisions. For investors who prefer a straightforward approach, this strategy can be quite attractive.
However, the lack of flexibility is a major downside. Static allocation doesn’t adjust to shifts in market volatility, meaning your portfolio’s risk exposure remains the same regardless of whether it aligns with current market conditions.
“One should not maintain a singular allocation strategy without regard to the equity volatility regime.” - Masao Matsuda, PhD, CAIA, FRM, President and CEO of Crossgates Investment and Risk Management
This rigidity essentially bets on your chosen allocation working under all market scenarios. While this might hold up over long periods, it can lead to increased volatility and reduced diversification benefits during times of market stress. Additionally, ignoring market signals about changing risk conditions could leave you exposed to unnecessary risk or cause you to miss opportunities to adjust your portfolio during turbulent periods.
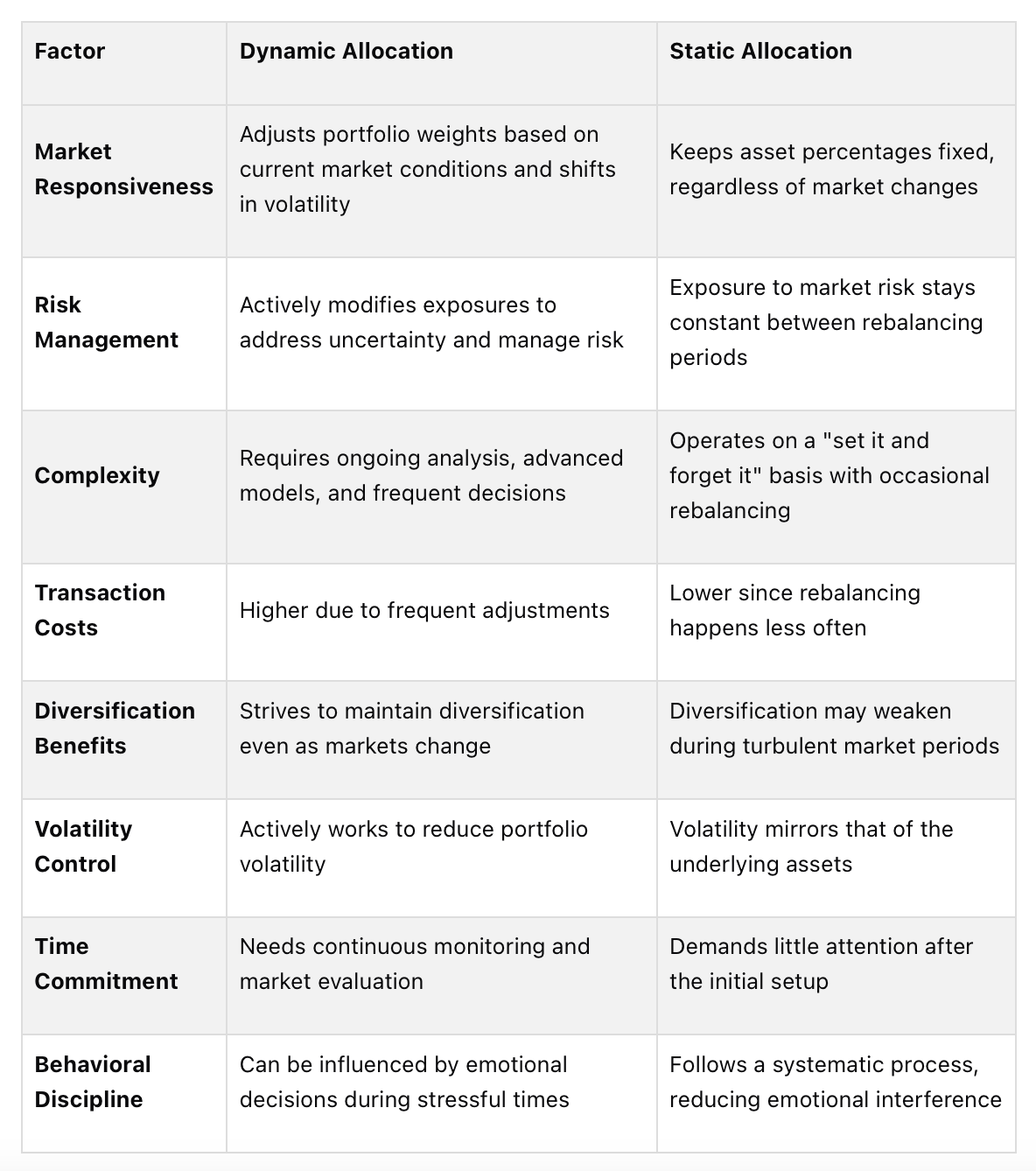
Side-by-Side Comparison: Dynamic vs. Static Allocation
Here’s a closer look at how dynamic and static allocation stack up in terms of risk management and implementation.
Comparison Table: Dynamic vs. Static
This breakdown highlights the main differences and how they can impact portfolio performance.
Which Strategy Performs Better?
When it comes to managing portfolio risk, dynamic allocation shines in volatile markets by actively adjusting to changing conditions. On the other hand, static allocation thrives on simplicity, offering a consistent and low-maintenance approach that works well in stable environments. However, dynamic allocation’s frequent adjustments can lead to higher transaction costs, potentially eating into its advantages. This makes the quality of implementation a crucial factor.
Ultimately, the decision between dynamic and static allocation depends on your personal preferences and capacity. Dynamic allocation requires advanced tools and constant market evaluation, making it more demanding. Meanwhile, static allocation is easier to manage over the long term, appealing to those who prefer a hands-off strategy.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Portfolio
Selecting an investment strategy requires a clear understanding of your goals, comfort with risk, and the time you can dedicate to managing your portfolio. These factors shape your investment profile, helping you build a portfolio that aligns with your needs and keeps you steady during market ups and downs.
Factors to Consider
If market volatility makes you uneasy, static allocation may be the way to go. This approach appeals to those who prefer simplicity and don’t want to constantly monitor the markets. It eliminates the need for frequent adjustments, offering a consistent and straightforward strategy. On the other hand, if you’re comfortable with market swings and want more control over your investments, dynamic allocation could be worth exploring, even though it requires more effort.
Your time horizon is another critical factor. For those with 20 or more years until retirement, dynamic strategies may be manageable since there’s ample time to recover from any downturns. However, if retirement is just around the corner - or you’re already there - the stability of static allocation might be more suitable. That said, it’s not a one-size-fits-all rule.
Dynamic allocation demands active market analysis, making it better suited for investors who enjoy tracking trends and have the expertise to make informed decisions. In contrast, static allocation works well for those with limited time to dedicate to their investments.
Transaction costs also play a role. Dynamic allocation involves frequent buying and selling, which can lead to higher fees that eat into your returns. Before going down this path, check if your broker offers low-cost trading and weigh whether the potential gains outweigh the additional expenses.
By considering these factors, you can create a systematic, rules-based approach that fits your needs.
Rules-Based Investing with The Predictive Investor
For U.S. investors looking for a middle ground, The Predictive Investor offers a structured, rules-based system that blends the stability of static strategies with the flexibility of dynamic ones. This method provides clear guidelines for adjusting your portfolio, helping you avoid emotional decision-making during turbulent markets.
This approach combines the consistency of static allocation with the adaptability of dynamic strategies. By following a set of rules, you can reduce emotional bias while still making strategic adjustments based on market conditions. Plus, it allows you to benefit from professional analysis without the need to constantly monitor the markets yourself.
The Predictive Investor also emphasizes high-growth, lesser-known stocks, helping you uncover opportunities that others might overlook. Whether you lean toward static or dynamic allocation, incorporating this targeted approach can enhance your overall strategy.
Finding Balance and Consistency
Many investors find success with a hybrid approach, which blends elements of both static and dynamic strategies. This method aims to strike the right balance between risk and return, offering a smoother investment experience.
For instance, allocating 10%–20% of your portfolio to a balanced risk strategy can help moderate risk while improving returns over time. The key is tailoring this balance to your comfort level and financial objectives.
If you’re unsure how to combine strategies, professional management can help. Hybrid funds, which actively adjust asset allocation based on market conditions, can provide a way to maximize returns while managing risks. When evaluating these funds, check that their strategy aligns with your goals, review their historical performance, and compare expense ratios.
No matter which approach you choose - dynamic, static, or hybrid - commit to it through all market conditions. Switching strategies based on short-term performance often leads to poor timing and lower returns. A disciplined and clear investment process is essential for long-term success.
Ultimately, the best strategy is the one you can stick with over time. A simple static allocation that you consistently maintain will often outperform a complex dynamic strategy abandoned during a market downturn.
Conclusion
Deciding between dynamic and static asset allocation boils down to understanding what suits your financial goals and personal comfort level. Each approach caters to different types of investors, with unique priorities and risk tolerances.
Key Takeaways
Here’s a breakdown of the core differences:
Static allocation is straightforward and requires minimal upkeep. It’s ideal for those who prefer a hands-off approach, allowing them to focus on other areas of life without worrying about frequent market changes.
Dynamic allocation offers flexibility and the possibility of higher returns, but it comes with added complexity, higher costs, and the need for active involvement. This approach is better suited for investors who enjoy managing their portfolios and have the knowledge to make informed adjustments.
Risk management varies significantly between the two. Static allocation embraces market ups and downs as part of a long-term strategy, while dynamic allocation seeks to mitigate risk by making tactical changes. Neither approach eliminates risk, but they handle it in different ways.
A hybrid approach can be a balanced option, combining the stability of static allocation with the adaptability of dynamic strategies. By keeping a core static portfolio and using a smaller portion for dynamic moves, you might reduce volatility while still taking advantage of market opportunities.
Transaction costs and tax implications are important considerations. Dynamic strategies often involve frequent trades, which can lead to higher fees and short-term capital gains taxes. These costs can significantly impact smaller portfolios where every dollar counts.
Final Thoughts
Ultimately, your investment strategy should reflect your risk tolerance, time horizon, and personal preferences - not fleeting market trends. No approach will work if you’re tempted to abandon it during challenging market conditions.
For those who prefer structure and discipline, rules-based investing can be a valuable framework. By removing emotional decision-making, it helps you stay focused on your long-term goals. Whether you go with static, dynamic, or hybrid allocation, having a clear plan keeps you grounded, even when markets are unpredictable.
In most cases, consistency beats complexity. A simple static strategy that you stick with through market cycles often outperforms an elaborate dynamic plan that’s abandoned when the going gets tough. The best strategy is one you can commit to over the long haul, regardless of market fluctuations.
Take the time to evaluate your situation, weigh your options, and choose an approach that aligns with your lifestyle and financial objectives. A disciplined strategy today can make a world of difference for your future self.
FAQs
What should I consider when deciding between dynamic and static asset allocation for my portfolio?
When choosing between dynamic and static asset allocation, think about your financial goals, your comfort level with risk, and how much effort you’re willing to put into managing your investments.
Dynamic allocation is all about flexibility. It adjusts your asset mix based on market conditions, aiming to balance returns and risks by reallocating as needed. This approach works well for investors who are okay with market ups and downs and enjoy an active role in managing their portfolios. On the flip side, static allocation sticks to a set asset mix aligned with a long-term plan. It’s a solid option for those who value consistency and prefer to make fewer adjustments over time.
The best approach depends on what you want to achieve financially, how much market fluctuation you can handle, and how involved you want to be in the process.
How do transaction costs and taxes impact the performance of a dynamic asset allocation strategy?
Transaction costs and taxes play a major role in shaping the results of a dynamic asset allocation strategy. The frequent rebalancing required by this approach can rack up expenses like brokerage fees and bid-ask spreads, which eat into the funds available for future investments.
Taxes, especially capital gains taxes on profits from rebalancing, can chip away at returns if not handled properly. Techniques like tax-loss harvesting can help offset some of these tax burdens. To get the most out of a dynamic strategy, it’s crucial to keep transaction costs in check and implement smart tax management practices.
Can combining dynamic and static asset allocation strategies help investors balance risk and reward more effectively?
Combining dynamic and static asset allocation strategies can create a more balanced approach to managing risk and reward in a portfolio. Static strategies focus on maintaining fixed allocations, offering a sense of stability. On the other hand, dynamic strategies adjust allocations based on market conditions, adding a layer of flexibility and adaptability.
When these two approaches are blended, investors can experience several benefits: reduced portfolio volatility, better diversification, and an opportunity to take advantage of market trends. This mix allows investors to harness the strengths of both strategies, improving risk management while aiming for stronger long-term performance.