Investor Sentiment: Tools for Market Analysis
Explore key tools for measuring investor sentiment, from the VIX to social media trackers, and learn how to use them for smarter trading decisions.
Investor sentiment reflects the emotions driving market behavior, often causing stock prices to deviate from their intrinsic value. Understanding and measuring sentiment can help investors identify potential market tops or bottoms. Key tools for sentiment analysis include:
Volatility Index (VIX): Tracks expected market volatility. High levels signal fear; low levels indicate confidence.
Put/Call Ratio: Measures bearish vs. bullish options activity. Extreme values often precede market reversals.
Fear and Greed Index: Combines seven indicators to assess market emotion on a 0-100 scale.
Social Media Sentiment Trackers: Analyze online discussions to gauge retail investor sentiment.
Introduction To Sentiment Analysis (4 Tools)
Key Tools to Measure Investor Sentiment
When you're trying to cut through the noise of the market, these tools can help you spot emotion-driven price moves that go beyond fundamentals. They rely on sentiment analysis frameworks to offer actionable insights.
Volatility Index (VIX)
Known as the "fear gauge", the VIX measures expected volatility in the S&P 500 over the next 30 days. It’s calculated using options prices and reflects how much uncertainty investors anticipate in the short term.
Here’s a quick guide to interpreting VIX levels:
Below 20: Indicates market confidence or complacency, with little expectation of major price swings.
20-30: Reflects normal market conditions and moderate uncertainty.
Above 30: Signals heightened fear, with significant volatility expected.
Above 40: Points to extreme fear and often marks capitulation.
Spikes in the VIX often coincide with selloffs, while low levels suggest bullish trends. For instance, when the VIX climbs above 40, it typically signals peak panic selling. On the flip side, a consistently low VIX (below 15) could hint at overconfidence, potentially setting up a market top.
Keep an eye on VIX divergences as well. If stocks are dropping but the VIX isn’t rising much, it could mean investors aren’t panicking yet - suggesting more downside may be ahead.
Put/Call Ratio
The put/call ratio compares the volume of bearish put options to bullish call options traded daily. It’s a handy way to gauge whether investors are leaning toward market declines or advances.
This ratio is calculated as:
Total Put Volume ÷ Total Call Volume
Using a 10-day moving average can help smooth out daily fluctuations.
Here’s how to read the numbers:
Below 0.7: Indicates extreme bullish sentiment, which could signal an overheated market and a potential sell-off.
0.7-1.0: Represents balanced sentiment with typical options activity.
Above 1.0: Suggests bearish sentiment, with more puts being bought than calls.
Above 1.2: Reflects extreme pessimism, often marking market bottoms.
This tool acts as a contrarian indicator - when sentiment leans too heavily in one direction, the market often moves the other way. For a more focused view, look at equity-only put/call ratios, which exclude index options. These provide a clearer picture of sentiment toward individual stocks rather than overall market hedging.
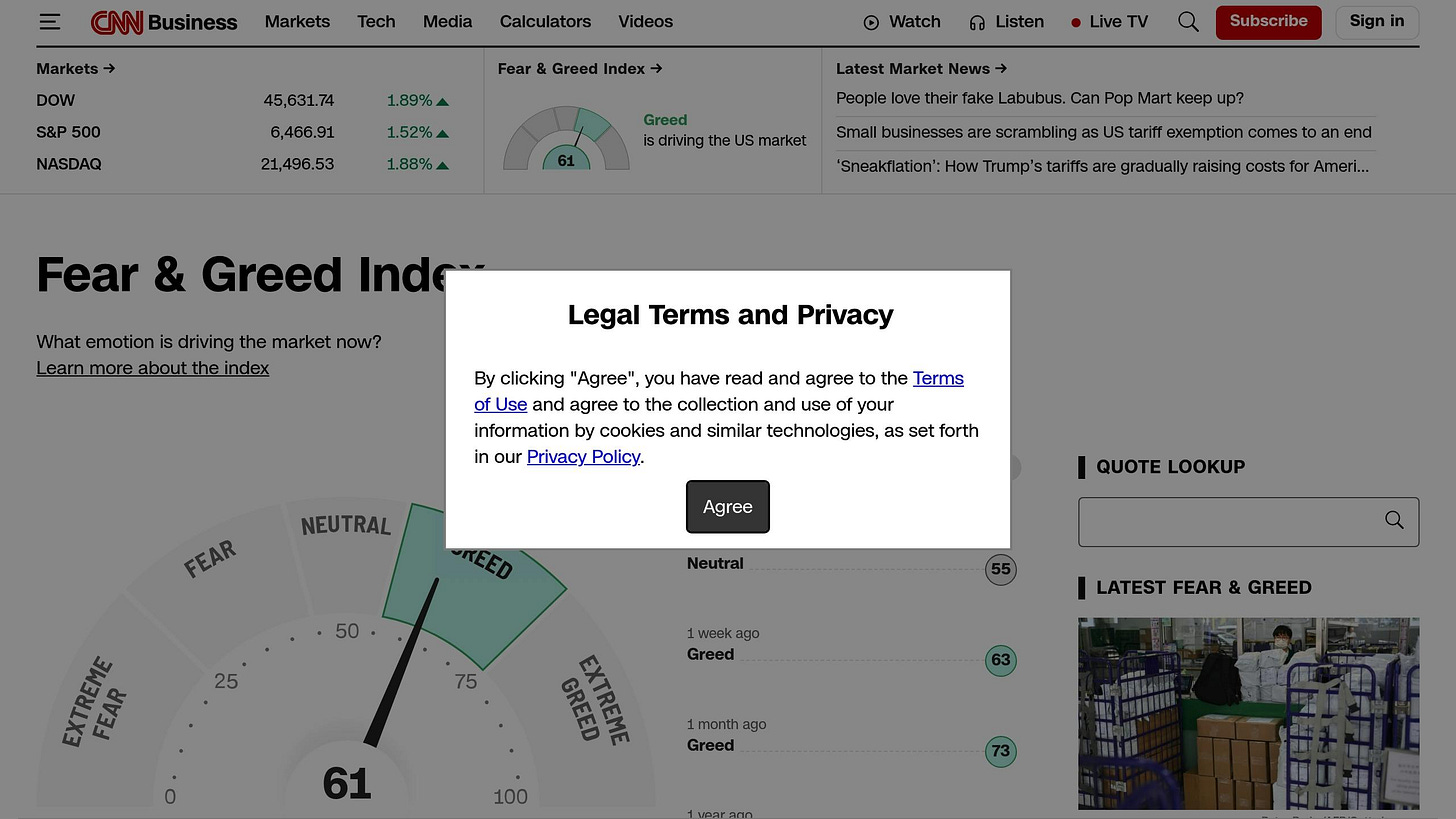
Fear and Greed Index
CNN’s Fear and Greed Index consolidates seven sentiment indicators into a single score ranging from 0 to 100. It’s designed to capture emotional extremes in the market by analyzing multiple data points.
The index incorporates factors like:
Stock price momentum: How far stocks are from their 52-week highs.
Stock price strength: The ratio of advancing to declining stocks.
Stock price breadth: Trading volume in advancing vs. declining stocks.
Put/call options ratio.
Junk bond demand: Reflecting risk appetite vs. a flight to safety.
Market volatility: Based on VIX levels.
Safe haven demand: Comparing the performance of stocks vs. bonds.
How to interpret the scores:
0-25: Extreme Fear, often signaling buying opportunities.
25-45: Fear, indicating market pessimism.
45-55: Neutral sentiment.
55-75: Greed, reflecting market optimism.
75-100: Extreme Greed, which could be a cue to sell.
The index is particularly useful when it reaches extremes - below 25 or above 75 - often aligning with short-term market reversals. However, these shifts can take weeks or months to fully play out.
Social Media Sentiment Trackers
With the rise of Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools, it’s now possible to analyze millions of social media posts to gauge real-time retail investor sentiment. These tools scan platforms like Twitter, Reddit, and StockTwits for mentions of stocks and market-related keywords.
Some key metrics to monitor include:
Mention volume: How often a stock is being discussed.
Sentiment score: Whether the tone of discussions is positive, negative, or neutral.
Trending topics: Identifying stocks gaining attention on social media.
Retail vs. institutional sentiment divergence: Highlighting gaps between social media chatter and traditional sentiment indicators.
Platforms like Reddit’s WallStreetBets have become influential, especially for small-cap stocks. A high volume of positive mentions can drive price moves. Similarly, Twitter sentiment analysis focuses on the tone of financial influencers and retail traders. Sudden shifts in sentiment or discussion volume often precede price movements, particularly for meme stocks and cryptocurrencies.
While social media sentiment can be volatile and prone to manipulation, it’s a useful supplement to traditional sentiment tools. For instance, a stock moving from negative to neutral sentiment online might hint at a potential reversal, even if the broader mood remains bearish. Use these insights alongside more established indicators for a well-rounded view.
How to Read Sentiment Data for Trading Decisions
Turn raw sentiment data into actionable trading insights by combining various data types effectively.
Number-Based Sentiment Analysis
Start with numerical indicators to establish clear thresholds before diving into qualitative signals.
Numerical sentiment indicators provide measurable benchmarks that can guide trading decisions. However, their true value lies in understanding them within the broader market context. Begin by defining baseline ranges for each indicator under normal market conditions. Then, watch for deviations from these norms as potential trading signals.
Take the VIX, for example. Instead of focusing solely on its absolute value, pay attention to its rate of change. A sharp rise in the VIX over a short period can signal a sudden shift in market sentiment, potentially forecasting significant price movements. On the other hand, a consistently high VIX often points to sustained market anxiety, which might offer opportunities to invest in strong stocks at lower prices.
Similarly, track the put/call ratio against a short-term rolling average. Large deviations, especially when paired with high trading volume, can indicate peak bearish sentiment and hint at a possible market reversal. Volume analysis adds another layer of clarity - an elevated put/call ratio combined with high trading volume could suggest that traders are rebalancing their positions, signaling potential turning points.
For a more comprehensive approach, combine multiple indicators into a single sentiment score. This unified metric can help you identify precise moments to adjust your trading positions swiftly and effectively.
Text-Based and AI Sentiment Analysis
Enhance numerical data with text-based insights to capture market subtleties.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools can transform qualitative text into actionable signals by focusing on factors like context, timing, and the credibility of sources.
News sentiment analysis is particularly useful when you monitor how quickly sentiment evolves. For example, sustained negative coverage across multiple outlets often signals increasing downward pressure on a stock or market. Tools that track sentiment momentum can help you differentiate between short-term reactions and longer-term shifts in market perception.
Look for mismatches between sentiment and price trends. For instance, if there's persistent positive sentiment around a stock while its price keeps falling, it may reflect unwarranted optimism. Conversely, ongoing negative sentiment despite rising prices could indicate that more experienced investors are quietly accumulating shares.
Earnings call sentiment analysis is another powerful tool. Subtle changes in management's tone - like increased use of cautious or hedging language - can sometimes precede downward revisions in guidance or weaker earnings in upcoming quarters.
Text analysis can also highlight sector rotation trends by tracking sentiment changes across industries. For example, if financial media begins to adopt a more optimistic tone toward defensive sectors while sentiment around growth sectors weakens, it may signal a broader shift in market conditions.
To ensure reliability, filter out bot activity and spam. Genuine sentiment changes often involve diverse language and emotional cues, while artificial manipulation tends to be repetitive and overly coordinated. Prioritize insights from verified accounts and reputable financial news sources.
Focus on sustained shifts in sentiment rather than brief spikes. For example, if negative sentiment about a company persists across news outlets, social media, and analyst reports over time, it could indicate deeper underlying issues. Cross-referencing these insights with complementary data - like options flow trends - can confirm whether a significant price move is likely. Use these refined signals to make timely adjustments to your trading strategy.
Using Sentiment to Time Market Cycles
Once you've mastered the basics of reading sentiment data, the next step is applying those insights to time market cycles. Market cycles often follow predictable emotional patterns, creating opportunities when sentiment swings wildly. This section dives into how extreme sentiment indicators can help you identify key turning points in the market.
Periods of extreme optimism often align with market peaks, while widespread fear and panic can signal potential bottoms. Recognizing these extremes is crucial for timing market reversals effectively.
Spotting Extreme Sentiment Levels
Identifying extreme sentiment can open the door to profitable trades, but it requires a disciplined and systematic approach.
Fear Extremes and Market Bottoms
When fear indicators spike across the board, it often reflects genuine panic in the market. Historically, sharp increases in fear indicators during crises have frequently preceded market recoveries, as panic selling gives way to stabilization.
Euphoria Extremes and Market Tops
Euphoria tends to creep in gradually. Watch for extended periods of low volatility, unusually low put/call ratios, and an abundance of overly optimistic media coverage or social media buzz. These are signs that market participants may be overly confident, which often precedes a peak. For instance, during certain market rallies, a surge in retail trading activity and a disregard for risk management have been early warning signs of an impending pullback.
Volume as a Confirmation Tool
Trading volume can validate sentiment extremes. For example, panic selling accompanied by unusually high volume often signals true capitulation, while a surge in buying volume during euphoric rallies confirms widespread participation. However, avoid relying on fixed volume thresholds alone. Instead, consider multiple indicators together to determine whether sentiment has reached an unsustainable extreme.
Sentiment Signals for Market Reversals
Beyond spotting extremes, analyzing divergences between sentiment and price action can help you identify potential reversals. These mismatches between sentiment and market behavior often hint at an upcoming shift in direction.
Bullish Divergences in Downtrends
When sentiment begins to improve even as prices continue to fall, it could indicate that selling pressure is easing. In such cases, savvy investors might start accumulating positions before prices fully reverse. For example, markets have sometimes hit new lows while sentiment indicators showed signs of stabilizing - an early clue that a recovery might be on the horizon.
Bearish Divergences in Uptrends
On the flip side, rising prices paired with worsening sentiment can be a red flag. This pattern often emerges when institutional investors quietly reduce their holdings while retail traders chase the upward momentum. Tracking insider selling alongside sentiment data can provide additional confirmation, as a disconnect between informed selling and uninformed buying often precedes a market correction.
Sector Rotation as a Sentiment Cue
Shifts in sentiment across sectors can also signal broader market changes. For instance, if investors begin favoring defensive sectors like consumer staples or utilities over growth-oriented ones, it may indicate growing concerns about economic uncertainty. Monitoring the relative performance of different sectors can provide valuable insights into the market's evolving sentiment landscape.
Timing Your Moves
While sentiment extremes are helpful for timing trades, they can persist longer than expected. Instead of trying to pinpoint the exact top or bottom, consider adjusting your positions incrementally. During periods of fear, gradually accumulate high-quality assets as sentiment stabilizes. Conversely, during euphoria, start taking profits in stages to protect your gains, even if prices continue to rise.
The most reliable reversal signals typically combine extreme sentiment with technical analysis. Look for situations where sentiment aligns with key support or resistance levels, or where momentum indicators show oversold or overbought conditions. This combination can provide the clarity needed to make well-informed decisions.
Adding Sentiment Analysis to Rules-Based Investing
To incorporate sentiment data into a rules-based framework, you can use these insights to enhance systematic decision-making.
Rules-based investing thrives on consistency and eliminates emotional biases. By integrating sentiment analysis, market sentiment can be converted into measurable rules. Objective indicators like market volatility, options activity, and social sentiment can guide investment actions, ensuring decisions remain methodical and free from second-guessing.
A disciplined approach treats sentiment metrics just like any other quantitative factor. Instead of relying on subjective market impressions, you can establish specific criteria that signal when to buy, sell, or adjust positions. This allows you to leverage market emotions in a structured way while preserving the consistency essential for successful investing.
Setting Up Sentiment Trading Triggers
When setting sentiment-based triggers, focus on widely recognized indicators. For instance, heightened market volatility often indicates increased fear, which could create buying opportunities for strong stocks. Similarly, shifts in options-based measures, such as the put/call ratio, can reveal changing sentiment. Prolonged pessimism might suggest a market bottom, while sustained optimism could indicate it’s time to take profits.
Social sentiment tools analyzing platforms like Twitter or Reddit can also be valuable. However, rather than reacting to short-term spikes, look for persistent extreme levels over several sessions. This filtering process helps you avoid acting on temporary noise and instead focus on meaningful market changes.
Combining Sentiment with Other Analysis Methods
Once you’ve established clear sentiment triggers, strengthen your strategy by integrating additional analysis methods.
Combining sentiment data with technical and fundamental indicators can provide a more complete picture. For example, if elevated market volatility coincides with an index nearing a major support level, the buying signal becomes much stronger than relying on either factor alone.
Fundamental analysis can also help distinguish between justified caution and overreaction. By focusing on companies with strong balance sheets, steady cash flow, and reasonable valuations, you can avoid making decisions based solely on sentiment. Additionally, tracking performance across various sectors can reveal whether a sentiment shift is isolated or part of a broader market trend.
To streamline this process, consider creating a scoring system that assigns weights to sentiment, technical, and fundamental indicators. Adjust your positions only when the combined score reaches a specific threshold, reducing the risk of false signals and improving decision accuracy.
Creating a Sentiment Tracking Routine
Establishing a routine for monitoring sentiment is crucial. Start by setting up a daily dashboard or spreadsheet to log key indicators like volatility metrics, options activity, and social sentiment levels.
In addition to daily tracking, review broader trends weekly. Pay attention to unusual options activity or insider trading data, as these can provide further context. Regular review sessions allow you to assess whether any triggers have been activated, refine your approach, and document your decisions for future reference.
To keep your strategy aligned with changing market conditions, periodically recalibrate your sentiment thresholds. This ensures your approach remains adaptable and consistent with a disciplined methodology. By quantifying sentiment shifts and updating your analysis regularly, you can maintain a systematic and effective investing strategy.
Conclusion: Using Sentiment Analysis for Better Investing
Investor sentiment analysis turns market emotions into actionable insights, helping you make smarter investment decisions. Tools like the VIX and the put/call ratio offer measurable ways to gauge market sentiment, replacing subjective guesswork with concrete data.
By using these tools, you can create a systematic approach that translates emotions into clear trading signals. The key is spotting market extremes before they reverse. For instance, when panic dominates the market, oversold quality stocks often present great buying opportunities. On the flip side, when euphoria peaks, it might be time to take profits or reduce your exposure.
Integrating sentiment analysis into a rules-based framework helps you set clear triggers, allowing for disciplined, emotion-free decisions. This approach eliminates the guesswork and ensures your strategy stays consistent.
When combined with technical and fundamental analysis, sentiment analysis becomes even more powerful. For example, if extreme fear aligns with strong support levels and solid fundamentals, your confidence in making a trade increases significantly.
The tools we've covered earlier enable a disciplined investment strategy. Building a routine around tracking sentiment keeps you in tune with market psychology without getting distracted by short-term noise. Regularly monitoring key indicators and documenting your observations can deepen your understanding of how sentiment cycles influence various sectors and stocks.
Ultimately, sentiment analysis allows you to benefit from predictable patterns in human behavior rather than being caught off guard by them. Markets are shaped by collective emotions, and quantifying these patterns gives you an edge for steady, long-term success.
Start with the essential indicators and refine your process as you grow more familiar with market sentiment.
FAQs
How can tools like the VIX and put/call ratio help identify potential market reversals?
Investor sentiment indicators like the VIX (Volatility Index) and the put/call ratio offer a window into market psychology, often hinting at potential turning points.
Take the VIX, for instance. When it spikes sharply - more than 20% above its 10-day average - it usually signals growing fear among investors. This heightened anxiety can sometimes precede a market bottom or even a reversal. On the other hand, the put/call ratio looks at the trading volume of put options compared to call options. A low ratio (below 0.7) points to optimism or bullish sentiment, while a high ratio (above 1.0) suggests bearish sentiment, often hinting at a possible market turnaround.
What’s particularly interesting is when these two indicators diverge. For example, a high VIX paired with a low put/call ratio can provide valuable clues about upcoming market shifts. By paying attention to these patterns, investors can position themselves more strategically and make decisions with greater confidence.
How does social media sentiment impact market trends, and is it as reliable as traditional indicators?
Social media sentiment offers a window into real-time investor emotions and public opinions, which can play a big role in shaping market trends. By diving into posts, comments, and discussions, investors can often spot emerging patterns or shifts in sentiment much faster than through traditional approaches.
That said, its reliability can vary when compared to more established indicators. Social media shines when it comes to quickly identifying trends and providing a wealth of data. But its predictive accuracy improves significantly when these trends remain steady over time and are backed by other analytical tools. To get the clearest picture of the market, social media sentiment is most effective when used alongside traditional methods like surveys, market indices, and economic reports. Together, they create a more balanced and informed perspective.
How can I use investor sentiment to improve a rules-based investing strategy?
Incorporating investor sentiment into a rules-based investing strategy can lead to more disciplined and informed decision-making. By blending sentiment data - such as insights gathered from news outlets, social media platforms, or other text-based sources - with technical indicators like moving averages or RSI, you can establish predefined rules that adapt to shifts in market sentiment.
For instance, if sentiment analysis reveals an optimistic outlook in the market, your strategy might include a rule to increase exposure to certain stocks. On the flip side, if sentiment turns negative, the system could pivot to a more cautious and defensive stance. This approach strengthens traditional models by integrating real-time public opinion, giving you an edge in navigating market trends.